|
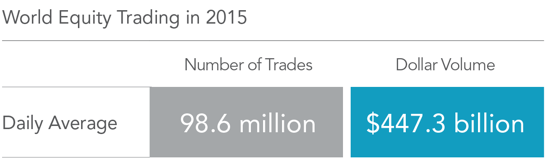
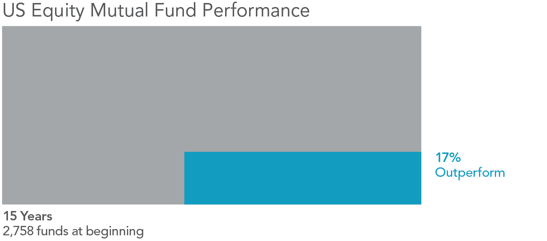
Over time we’ve learned much from financial science and the forces or factors that help to explain where expected returns come from. The momentum factor identifies the tendency for positively/negatively performing assets to continue their positive/negative trajectory for a short amount of time into the future. Essentially the “winners” tend to stay winners and the “losers” tend to stay losers for a period of time. So what does the research suggest and how can investors benefit? First a bit of background: The momentum effect, first written about in the early 1990’s, leaves efficient market hypothesis (EMH) proponents such as myself with a realism that’s hard to rectify. For EMH advocates price is king. In laymen’s terms: The best judge of any particular assets inherent worth is its current price, thanks to the millions of market participants (buyers and sellers) actively voting with their dollars. Momentum on the other hand contradicts this notion, at least over the short term. Why does it exist? The majority of factors that we target in building portfolios commonly have a risk based explanation for their performance, i.e. stocks outperforming bonds, small companies outperforming large companies or value outperforming growth over time. Attempting to explain the momentum factor’s performance through the conventional risk based lens is difficult. Like these other factors, momentum has been persistent across time, asset classes and geography. However, its performance is best explained from a behavioral perspective. Other theories exist as to why winners stay winners and losers stay losers for a period of time, but the idea that investors tend to either over react or under react to news is a leading hypothesis. This suggests that markets aren’t perfectly efficient, a point to which I would begrudgingly agree. Perfectly being the key word. While over long periods of time, markets usually get it right, in short spurts security prices seem to have a bit of “noise” built into them. The investment application of momentum When looking at the addition of any factor to a portfolio, investors should always start out as cynics, requiring large amounts of supporting evidence. First, academia must backup its inclusion with rigorous empirical research. Second, it can’t just look good on paper. Practical application dictates that investors must be able to capture the performance after any additional costs associated with targeting it. For a long time, this was a key issue with incorporating the momentum factor. Due to the frequent changes to the winners and loser’s categories, does the increased trading cost associated with buying and selling surpass the benefit? Furthermore, does its inclusion dilute the all-important diversification of the portfolio? Not only must an investment vehicle exist, but the right vehicle has to be selected from a universe of thousands. Adding further complexity, is how it interacts and/or complements the rest of the portfolio. We believe that momentum is most effectively targeted through a low cost, quantitative, rules based methodology. This approach helps to lower cost and improve overall portfolio diversification. Investors commonly associate diversification with the benefits of different sizes and styles of asset classes which don’t always move in the same direction under different market conditions. Well, the same logic can in certain instances be applied to diversifying exposure to factors. Such is the case when momentum is properly paired with value due to their negative correlations with each other. In sum, momentum has the ability to offer long term performance and diversification benefits when it is properly implemented. As a firm that specializes in factor based investing we remain dedicated to research and the practical application of it. This translates into ever evolving, globally diversified portfolios which target areas that drive expected return. In 1958, economist Leonard Read published an essay entitled “I, Pencil: My Family Tree as Told to Leonard E. Read.” The essay, narrated from the point of view of a pencil, describes the “complex combination of miracles” necessary to create and bring to market the commonplace writing tool that has been used for generations. The narrator argues that no single individual possesses enough ability or know-how to create a pencil on their own. Rather, the mundane pencil—and the ability to purchase it for a “trifling” sum—is the result of an extraordinary process driven by the knowledge of market participants and the power of market prices. THE IMPORTANCE OF PRICE Upon observing a pencil, it is tempting to think a single individual could easily make one. After all, it is made up of common items such as wood, paint, graphite, metal, and a rubber eraser. By delving deeper into how these seemingly ordinary components are produced, however, we begin to understand the extraordinary backstory of their synthesis. Take the wood as an example: To produce wood requires a saw, to make the saw requires steel, to make steel requires iron. That iron must be mined, smelted, and shaped. A truck, train, or boat is needed to transport the wood from the forest to a factory where numerous machines convert it into lumber. The lumber is then transported to another factory where more machines assemble the pencil. Each of the components mentioned above and each step in the process have similarly complex backstories. All require materials that are sourced from far-flung locations, and countless processes are involved in refining them. While the multitude of inputs and processes necessary to create a pencil is impressive, even more impressive are the coordinated actions required by millions of people around the world to bring everything together. There is the direct involvement of farmers, loggers, miners, factory workers, and the providers of capital. There is also the indirect involvement of millions of others—the makers of rails, railroad cars, ships, and so on. Market prices are the unifying force that enables these millions of people to coordinate their actions efficiently. Workers with specific knowledge about their costs, constraints, and efforts use market prices to leverage the knowledge of others to decide how to direct their own resources and make a living. Consider the farmer, the logger, and the price of a tree. The farmer will have a deep understanding of the costs, constraints, and efforts required to grow trees. To increase profit, the farmer will seek out the highest price when selling trees to a logger. After purchasing the trees, the logger will convert them to wood and sell that wood to a factory. The logger understands the costs, constraints, and efforts required to do this, so to increase profit, the logger seeks to pay the lowest price possible when buying trees from the farmer. When the farmer and the logger agree to transact, the agreed upon price reflects their combined knowledge of the costs and constraints of both growing and harvesting trees. That knowledge allows them to decide how to efficiently allocate their resources in seeking a profit. Ultimately, it is price that enables this coordination. On a much larger scale, price formation is facilitated by competition between the many farmers that sell trees to loggers and between the many loggers that buy trees from farmers. This market price of trees is observable and can be used by others in the production chain (e.g., the lumber factory mentioned above) to inform how much they can expect to pay for wood and to plan how to allocate their resources accordingly. THE POWER OF FINANCIAL MARKETS There is a corollary that can be drawn between this narrative about the market for goods and the financial markets. Generally, markets do a remarkable job of allocating resources, and financial markets allocate a specific resource: financial capital. Financial markets are also made up of millions of participants, and these participants voluntarily agree to buy and sell securities all over the world based upon their own needs and desires. Each day, millions of trades take place, and the vast collective knowledge of all of these participants is pooled together to set security prices. Exhibit 1 shows the staggering magnitude of participation in the world equity markets on an average day in 2015. In US dollars. Global electronic order book (largest 60 exchanges). Source: World Federation of Exchanges. Any individual trying to outguess the market is competing against the extraordinary collective wisdom of all of these buyers and sellers. Viewed through the lens of Read’s allegory, attempting to outguess the market is like trying to create a pencil from scratch rather than going to the store and reaping the fruits of others’ willingly supplied labor. In the end, trying to outguess the market is incredibly difficult and expensive, and over the long run, the result will almost assuredly be inferior when compared to a market-based approach. Professor Kenneth French has been quoted as saying, “The market is smarter than we are and no matter how smart we get, the market will always be smarter than we are.” One doesn’t have to look far for data that supports this. Exhibit 2 shows that only 17% of US equity mutual funds have survived and outperformed their benchmarks over the past 15 years. Beginning sample includes funds as of the beginning of the 15-year period ending December 31, 2015. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. Source: Dimensional Fund Advisors, “The US Mutual Fund Landscape.” See disclosures for more information. CONCLUSION The beauty of Leonard Read’s story is that it provides a glimpse of the incredibly complex tapestry of markets and how prices are formed, what types of information they contain, and how they are used. The story makes it clear that no single individual possesses enough ability or know-how to create a pencil on their own but rather that the pencil’s miraculous production is the result of the collective input and effort of countless motivated human beings. In the end, the power of markets benefits all of us. The market allows us to exchange the time we require to earn money for a few milliseconds of each person’s time involved in making a pencil. For an investor, we believe the lesson here is that instead of fighting the market, one should pursue an investment strategy that efficiently and effectively harnesses the extraordinary collective power of market prices. That is, an investment strategy that uses market prices and the information they contain in its design and day-to-day management. In doing so, an investor has access to the rewards that financial markets make available to providers of capital. Leonard Read’s essay can be found here: http://econlib.org/library/Essays/rdPncl1.html.
Source: Dimensional Fund Advisors LP. There is no guarantee investment strategies will be successful. US-domiciled mutual fund data is from the CRSP Survivor-Bias-Free US Mutual Fund Database, provided by the Center for Research in Security Prices, University of Chicago. Certain types of equity funds were excluded from the performance study. Index funds, sector funds, and funds with a narrow investment focus, such as real estate and gold, were excluded. Funds are identified using Lipper fund classification codes. Correlation coefficients are computed for each fund with respect to diversified benchmark indices using all return data available between January 1, 2001, and December 31, 2015. The index most highly correlated with a fund is assigned as its benchmark. Winner funds are those whose cumulative return over the period exceeded that of their respective benchmark. Loser funds are funds that did not survive the period or whose cumulative return did not exceed their respective benchmark. All expressions of opinion are subject to change. This article is distributed for informational purposes, and it is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, recommendation, or endorsement of any particular security, products, or services. Ken French is a member of the Board of Directors for and provides consulting services to Dimensional Fund Advisors LP. |
By Tim Baker, CFP®Advice and investment design should rely on long term, proven evidence. This column is dedicated to helping investors across the country, from all walks of life to understand the benefits of disciplined investing and the importance of planning. Archives
December 2023
|
|
Phone: 860-837-0303
|
Message: [email protected]
|
|
WINDSOR
360 Bloomfield Ave 3rd Floor Windsor, CT 06095 |
WEST HARTFORD
15 N Main St #100 West Hartford, CT 06107 |
SHELTON
One Reservoir Corporate Centre 4 Research Dr - Suite 402 Shelton, CT 06484 |
ROCKY HILL
175 Capital Boulevard 4th Floor Rocky Hill, CT 06067 |
Home I Who We Are I How We Invest I Portfolios I Financial Planning I Financial Tools I Wealth Management I Retirement Plan Services I Blog I Contact I FAQ I Log In I Privacy Policy I Regulatory & Disclosures
© 2024 WealthShape. All rights reserved.